| AUFGABEN zu Differential-/Integralrechnung |
| [ I N H A L T ] | [ MATHEMATIK Übersicht ] |
Aufgaben zu
13. Winkelfunktionen
13.7 Lineare Approximation der sin-Funktion
13.8 Die Ableitung weiterer Winkelfunktionen und ihrer Umkehrung
| arccot ' y = - | 1 | |
| 1 + y² |
| a. | y = 3 sin 2 x | b. | y = - 2 cos ( 3 x + |
c. | y = sin² x | ||
| d. | y = cos² x | e. | y = cosn (x) | f. | y = tan² x | ||
| g. | y = tan 3 x² | h. | y = tan² ( cos x ) | i. | y = cot ( 3 x + 5 ) | ||
| k. | y = |
l. | y = 3 x + tan 3x | m. | y = 2 sin² 3x | ||
| n. | y = sin³ x/3 - 3 sin x/3 | o. | y = x² sin x | p. | y = x tan x |
| a. | y = arcsin x/2 | ||
| b. | y = 1/3 arctan x/3 | ||
| c. | y = arccos 2x | ||
| d. | y = arccot 2/x + arctan x/2 | ||
| e. | y = arctan | x - 1 | |
| x + 1 | |||
| f. | y = arcsin | x - 1 | |
| x + 1 | |||
| g. | y = x · arcsin x +
|
||
| h. | y = x · ( arcsin x ) ² - 2 x +
|
||
| i. | y = x · arccos 2x -
½ |
||
| a. | y = sin x - sin³ x | b. | y = sin 2x + 2 cos x | |||||
| c. | y = 4 sin x + | 1 | d. | y = | 2 sin x + 1 | |||
| sin x | sin x + 2 | |||||||
| e. | y = x sin x | f. | y = x + sin x | |||||
13.9 Stammfunktionen der Winkelfunktionen
| a. | sin x dx | b. | sin 2x dx | |||||
| 0 | 0 | |||||||
| c. | 2 |
( cos x + sin x ) dx | d. | 2 |
sin² x dx ( sin² x = ½ ( 1 - cos 2x ) ) | |||
| 0 | 0 | |||||||
| e. | 10 | 1 | dx | f. | 1 | 1 | dx | |
| 1 + 4 x² | 9 + x² | |||||||
| 0 | 0 | |||||||
| g. | 2 | dx | h. | a/2 | dx | |||
| 0 | 0 | |||||||
| a. | sin 18° | b. | cos 1° | c. | sin 80° | d. | cos 162° |
| a. | y = sin x ; y = x ; y = x - x3/6 und y = x - x3/6 + x5/120 |
| a. | y = cos x ; y = 1 - ½ x² ; y = 1 - ½ x² + 1/24 x4 |
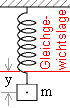
Für die Kraft F gilt also
| F | = - D · y , | |
| wobei D eine Konstante ist, die allein von der Feder abhängt. Jede Bewegung mit diesem linearen Kraftgesetz heißt | ||
| " harmonische Schwingung " . | ||
| Kraft ist gleich Masse mal Beschleunigung. Beschleunigung ist die 2. Ableitung der Wegfunktion y nach der Zeit, also y '' (t) . Daher ist für harmonische Schwingungen |
||
| ( 1 ) | = - D · y (t) | |
| Hier liegt eine Differentialgleichnung vor. Sie stellt die Aufgabe, Funktionen f zu suchen, die Gleichung ( 1 ) erfüllen, d.h. für die | ||
| m · f '' | = - D · f ist. | |
| Zeige, dass y = sin |
||
| wenn | ist. | |
| ( |
||
| Es ist | , wobei T die Schwingungsdauer bedeutet. Damit ist | |
| |
. ) | |
weitere Aufgaben zu
14. Exponential- und Logarithmusfunktionen
![]()